
Communication/Marketing, Art Direction
ÉTHOLOGY GRAPHIC DESIGN
Exprimer l'animalité ou l'humanité
Définition
Animality encompasses all the characteristics that define an entity as belonging to the animal kingdom. Physiological as well as behavioral traits testify to this belonging.
Ethology is the science that studies animal behavior. Its conclusions are often used for comparative purposes with humans, to either refute or confirm theories arising from psychology.
Personification is a figure of speech that attributes human properties or behaviors to an animal or thing.
BRIEF
You will produce a piece of work highlighting a reversal of behavior: animals towards humans or vice versa. Animals behave like humans, and humans like beasts. Your work will showcase, in both staging and writing, this alteration, for better or for worse.
Brainstorming

Axe 1 : personnaification
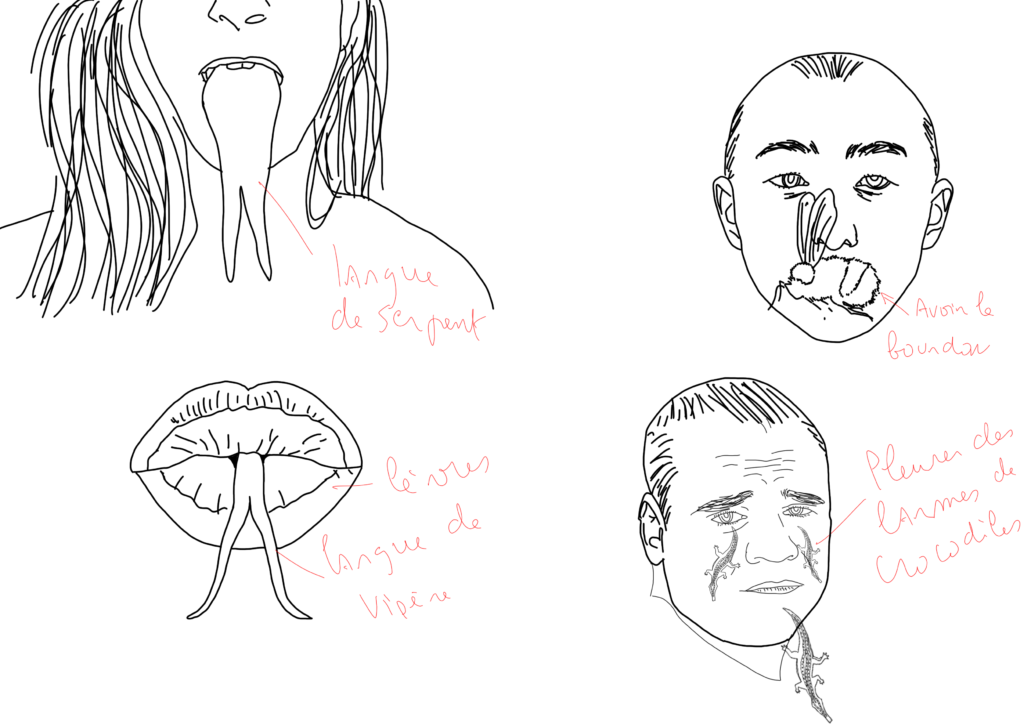
Who in our society hasn’t heard expressions like ‘you have a snake’s tongue’, ‘you eat like a pig’… The use of expressions related to animals personifies humans, but the reverse also exists.
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human behavioral or morphological characteristics to other entities such as gods, animals, objects, phenomena, ideas, and even beings from another world where applicable.
Examples include animals and plants, as well as forces of nature like wind, rain, or the sun being described as having human motivations or possessing the ability to understand and reflect. In literature, this is referred to as ‘personification’.
At the beginning of human behavioral modernity in the Upper Paleolithic era, around 40,000 years ago, examples of zoomorphic works (with animal-like appearance) represent the idea of anthropomorphism. One of the most well-known of these works is the ivory sculpture of the Lion Man, a human figure with the head of a lion, dating back 40,000 years. Anthropomorphism is sometimes used to talk about humans, for example in the fables of Aesop or Jean de La Fontaine, in the ‘Roman de Renart’, in many Walt Disney cartoons, etc.
The opposite of anthropomorphism is dehumanization, ‘to make an individual, a group lose its human character, to take away all generosity, all sensitivity from it’. Dehumanization can occur in different contexts such as intergroup conflicts, but it can also be illustrated in classic everyday social phenomena, like moral disengagement. Dehumanizing behavior doesn’t necessarily require a racist or xenophobic ideology to manifest…
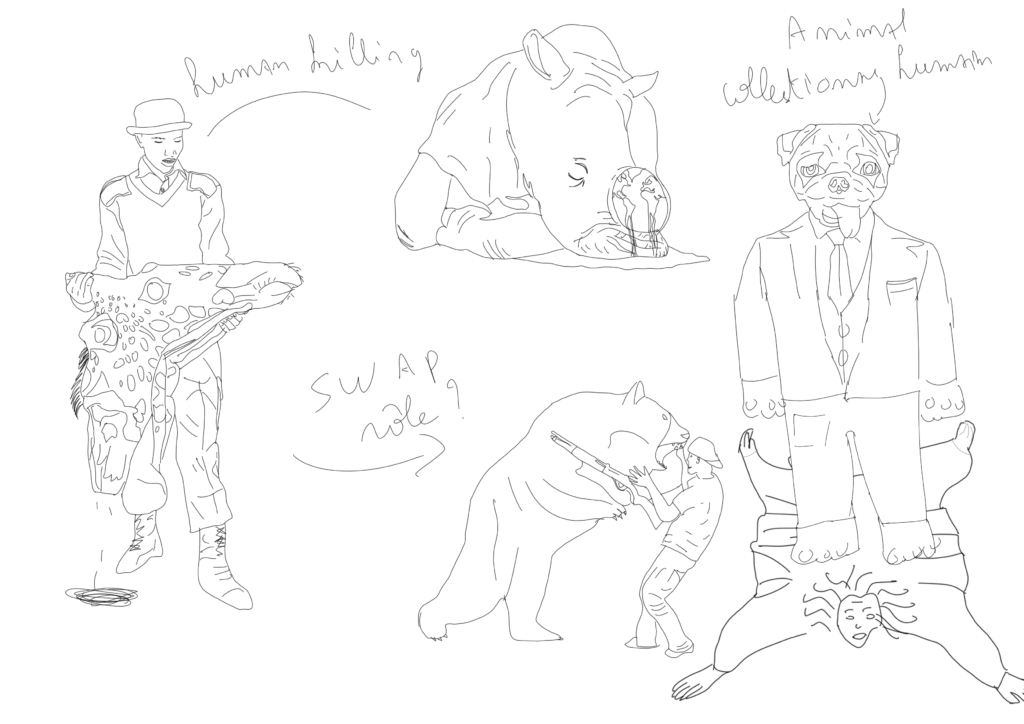
Axe 2 : Hunt
Hunting is the pursuit of animals with the intention of capturing or killing them, either for consumption, sustenance, or destruction. When hunting is subject to regulation, engaging in hunting outside of its legal framework is termed poaching. Destruction operations are subject to the right of destruction, which differs in part from the right of hunting. Cynology is the art of hunting. Originally, hunting served as a source of meat but also provided various resources such as skin, fur, horn, antlers, bone, tendons, teeth, etc. Hunting is an intriguing subject: for both us and animals, it’s about obtaining food to survive, yet in our time, this behavior is drastically changing. By this, I mean that many factors contribute to the cessation of hunting (particularly factories). However, the negative type of hunting is POACHING, which endangers many protected animal species, hunted for something that characterizes them. The hunter becoming the hunted by his prey is a recurring theme in literature. Thus, Actaeon, a famous hunter of ancient Greece, is transformed into a deer fleeing from his own hounds who do not recognize him. From hunter, Actaeon becomes prey. Ovid writes about him in the Metamorphoses: ‘His hounds caught sight of him (…). This ravenous pack (…) pursued the young man (…). He flees in the same places where he has so often pursued game; alas, yes, he flees those who were in his service.’ The metamorphoses of the hunter into prey are not unknown in the Middle Ages. In the margins of Gothic manuscripts with humorous drawings, the illuminations substitute the hunter for the hunting dog, the rabbit, and above all, the monkey. Alternatively, the hunter or his dogs are substituted for the game. The falconer monkey is often depicted perched on a donkey holding not a falcon but an owl. The owl is one of the most despised birds of the Middle Ages and shares with the monkey a reputation for physical and moral ugliness.


Axe 3 : law of the jungle
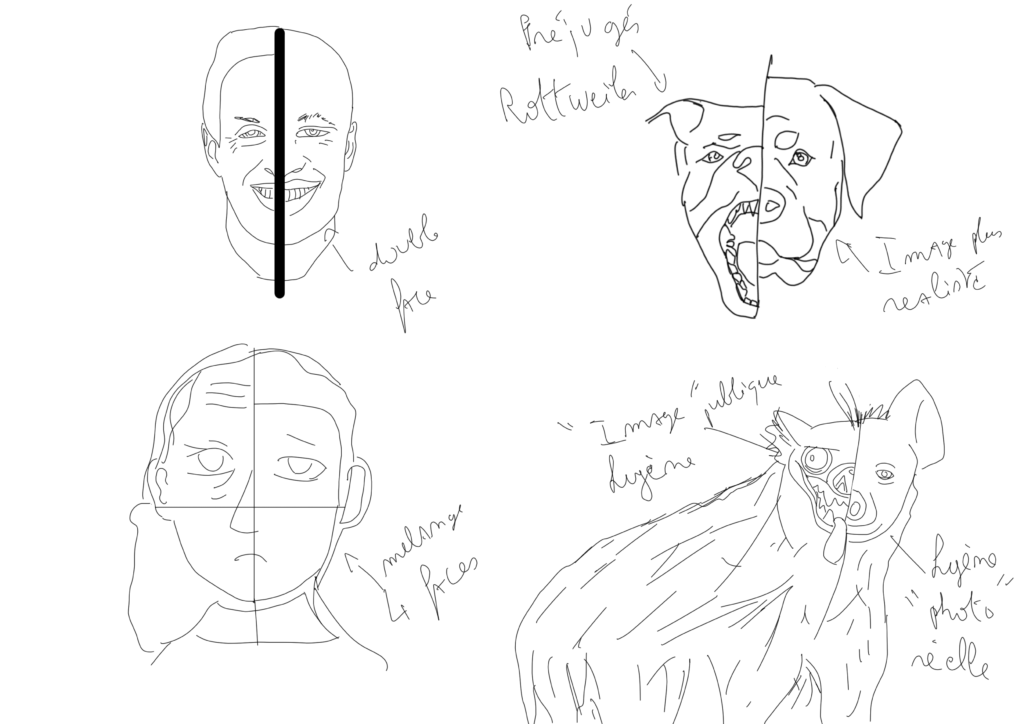
The law of the jungle refers to a situation where a confrontation is resolved through a balance of power in favor of one party and to the detriment of another. For human society, we can draw a parallel with discrimination: unfortunately, it’s a common issue, stemming from differences, divergent opinions…
Similarly, in the animal kingdom, there is also a form of discrimination regulated by ‘the law of the jungle’. This means that only the strongest will survive because they represent the law. For example, in lion society, there is one male for a large number of females, so if a small male is born, it may die immediately if the lion considers that his kingdom is going to be ‘challenged’.
Likewise, for pandas, out of a group of babies, only one will be raised because the panda, not knowing if it will be able to raise more, decides to choose only one (to ensure its survival). We could also link this part to prejudices; for hyenas, the first idea that comes to mind is probably scavenger, corpse eater… And yes, they have unwittingly been given a bad role; in ‘The Lion King’, they play the role of villains, with sinister laughter and devious ideas. However, hyenas are intelligent animals that are more akin to lions or dogs…
The same goes for Rottweilers; human society considers them dangerous dogs and thus avoids them. However, they are animals that mostly learn from their master; if the master is not good, the dog can never become good either
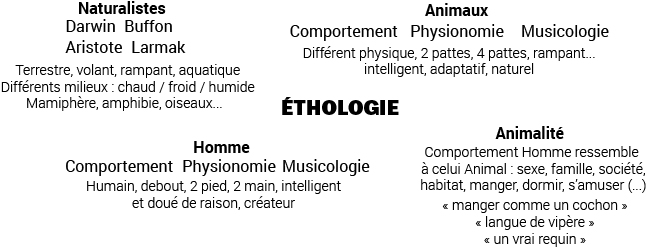
Axe 4 : Canibalism
Cannibalism is a practice that involves consuming (completely or partially) an individual of one’s own species. It’s important to differentiate cannibalism from the term ‘Anthropophagy,’ which refers specifically to the practice of consuming human flesh. Anthropophagy is a form of cannibalism but is limited to humans.
Cannibalism is studied by ethnologists and anthropologists, sometimes within the framework of a specific culture or society (such as Hélène Clastres for the Tupinamba, or Marcel Detienne for Greece). In human society, one of the most well-known instances is the story of Uruguayan Air Force Flight 571 in 1972. This plane crashed in the Andes Mountains. Out of the 45 passengers and crew members, 17 died within 24 hours of the crash, and 12 more within the following two months. To survive, the survivors resorted to consuming the bodies of the deceased passengers, preserved by the cold…
In the animal kingdom, many species consume their own kind, but various types of cannibalism can be identified, including:
- Survival cannibalism (which allows an individual to survive in harsh habitats, for example, tadpoles or coconut crabs).
- Sexual cannibalism (when an individual consumes its sexual partner during or after mating, a technique useful for recovering the energy needed for egg-laying. This form of cannibalism can be found in certain spiders, the praying mantis, or the female brown streamlet damselfly).
- Parental or filial cannibalism (used to combat overpopulation, food shortages, diseases, etc. This can be observed in many rodents, corals or clams, bees, or numerous aquatic species).
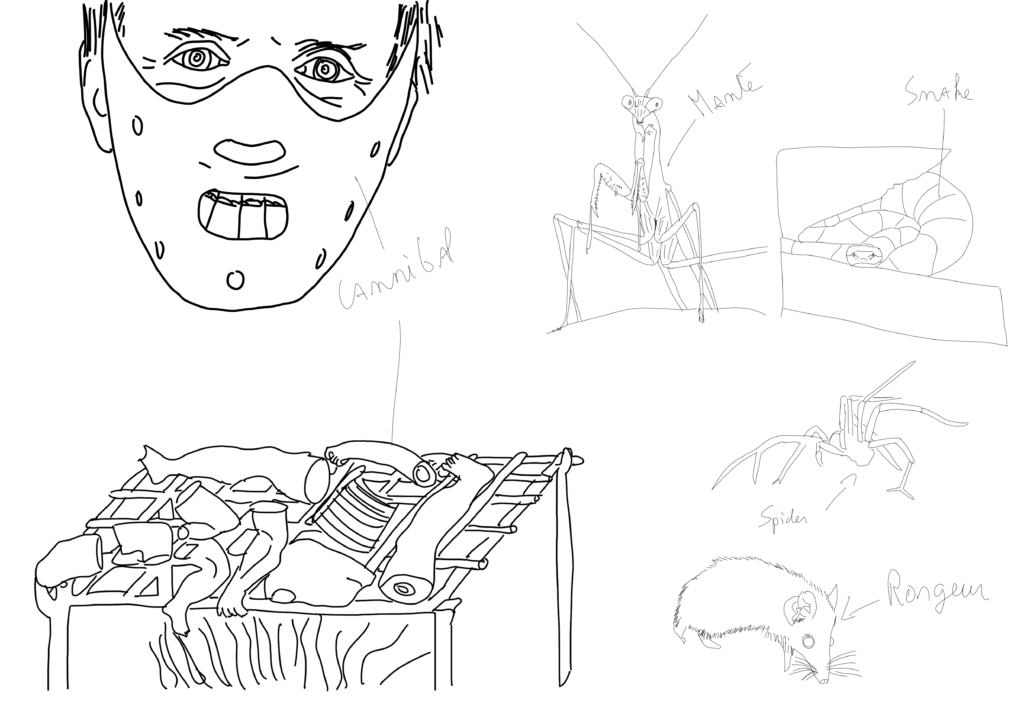
Axe 5 : Foster care
What do we call foster care? This topic, relevant to both animal and human species, describes behaviors related to ‘abandoning’ offspring in locations where they can survive with the assistance of another individual.
In human society, many babies are abandoned by their parents, for various reasons, good or bad, with the aim of finding them foster families. These families will care for them until they are capable of living independently.
In the animal kingdom, let’s take birds as an example. Brood parasitism refers to the behavior of laying eggs in the nests of other individuals, whether of the same species or not, thereby benefiting from the food intended for the entire brood. The most well-known example is that of the Common Cuckoo, which parasitizes the nests of various species of passerine birds, pushing out the other nestlings.
This behavior has also evolved in other species, including salamanders, fish, and even insects.
Axe choisit : la chasse
And what if we swapped roles?
In this approach, we’ll play with a metamorphosis of prey into hunter and hunter into prey.
We’ll also seek to highlight this idea by criticizing poaching, which is entirely illegal, as well as the market linked to poaching (illegal fur trade, organized hunting, etc.).
This approach will feature 3 posters addressing different closely related topics.

